What is a PCB Board? Understanding Types, Functions, and Applications
The world of electronics is intricately tied to a fundamental component known as the PCB board, or printed circuit board. These essential structures serve as the backbone of electronic devices, facilitating the connection and functionality of various components. Dr. Emily Chen, a renowned expert in electronic engineering, once stated, "The PCB board is not just a platform; it is a critical element that determines the performance and reliability of electronic systems." This highlights the significance of understanding the different types, functions, and applications of PCB boards in modern technology.
As we delve into the nuances of PCB boards, we uncover their variations, ranging from single-layer to multi-layer designs, each tailored to specific applications in industries from consumer electronics to aerospace. The versatility of PCB boards enables them to accommodate increasingly complex electronic circuits, making them indispensable in driving innovations in technology. From mobile devices to medical equipment, the role of PCB boards cannot be overstated, as they empower devices to operate efficiently and effectively.
In this exploration, we will demystify the different types of PCB boards, their fundamental functions, and the myriad applications that underscore their importance in today's fast-paced technological landscape. Understanding these elements not only enriches our knowledge of electronics but also paves the way for future advancements in the industry.
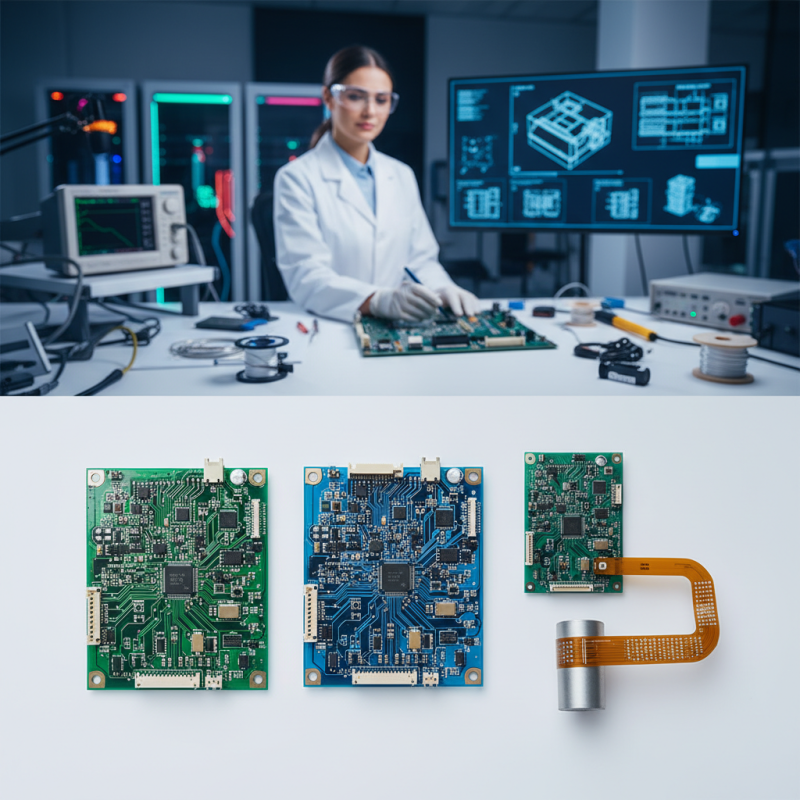

Understanding the Basics of PCB Boards: Definition and Importance
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in the modern electronics landscape, serving as the backbone for almost all electronic devices. A PCB is a flat board made of insulating material that houses conductive pathways, allowing electronic components to connect and function efficiently. The importance of PCBs lies in their ability to compactly organize components, reducing the risk of circuit shorting and making mass production more feasible. Without PCBs, the intricate electronic devices we rely on today would merely be a collection of disconnected parts.
When considering a PCB, it's essential to understand the various types and their specific applications. There are single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer PCBs, each tailored for different purposes ranging from simple electronics to complex systems. For instance, single-sided PCBs are commonly found in low-cost applications, while multi-layer boards are used in sophisticated electronic devices, such as computers and smartphones, where space is at a premium.
Tips for working with PCBs include ensuring compatibility with the chosen components and meticulously designing the layout to minimize electromagnetic interference. Additionally, it's advisable to conduct thorough testing during the prototyping phase to identify potential issues early on. This proactive approach can save time and resources in the long run, ensuring a seamless transition into production.
Different Types of PCB Boards and Their Unique Characteristics
PCB boards, or printed circuit boards, come in various types, each designed to fulfill specific functions within electronic devices. One of the most common types is the single-sided PCB, which has conductive pathways on one side and is ideal for simple, low-density applications. Single-sided PCBs are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making them a popular choice for basic consumer electronics and simple circuit designs.
Another widely used type is the double-sided PCB, which features conductive layers on both sides. This allows for more complex circuitry and higher component density, making double-sided PCBs suitable for applications like power supplies and more sophisticated electronic devices. Additionally, multi-layer PCBs, comprising three or more layers of circuitry, are designed for advanced applications requiring high performance, such as computer motherboards and high-frequency devices. These various types of PCBs cater to different needs, enabling innovation and efficiency across countless electronic applications.
Types of PCB Boards and Their Unique Characteristics
Key Functions of PCB Boards in Electronic Devices and Systems
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) play an essential role in modern electronic devices and systems, serving multiple key functions that enhance performance and reliability. One of the primary functions of a PCB is to provide a foundation for electrical components. By ensuring that components are arranged in a specific layout, PCBs facilitate efficient electrical connections, reducing the risk of short circuits and signal interference. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global PCB market size is projected to reach $87.3 billion by 2027, highlighting the critical importance of these boards in various sectors including consumer electronics, telecommunications, and automotive applications.
In addition to supporting electrical components, PCBs also enable thermal management within electronic devices. This is particularly vital as electronic devices become more compact and powerful, generating excess heat that can lead to malfunctions or reduced lifespan. Efficient heat dissipation designs integrated into PCBs help maintain optimal temperatures, thus ensuring longevity and performance. The IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries) outlines design strategies that can improve thermal performance, with studies showing that proper thermal management can increase component life by up to 50%.
Tip: When designing or selecting a PCB, consider the layer count and material used, as these factors significantly impact both signal integrity and thermal management. A thorough understanding of your device’s power requirements can also help determine the right PCB specifications, ultimately contributing to enhanced performance and reliability.
What is a PCB Board? Understanding Types, Functions, and Applications
| Type of PCB | Function | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided PCB | Basic circuit connections, suitable for low-density designs | Consumer electronics, basic devices |
| Double-Sided PCB | Allows for more complex designs with components on both sides | Power supplies, amplifiers |
| Multilayer PCB | High-density designs, facilitates intricate interconnections | Computers, advanced communication devices |
| Flexible PCB | Bends and conforms to the design, saving space | Wearable devices, medical equipment |
| Rigid-Flex PCB | Combination of rigid and flexible substrates, enhances design flexibility | Smartphones, aerospace applications |
Common Applications of PCB Boards Across Various Industries

PCB (Printed Circuit Board) boards are integral components in a multitude of industries, providing the necessary framework for electronic circuitry. With the global PCB market projected to reach approximately $85.23 billion by 2027, it's evident that their applications span a wide range of sectors. In the automotive industry, PCBs are essential for managing electronic systems, from engine control units to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). The increasing integration of smart technology in vehicles is driving demand; reports suggest that the automotive PCB market alone could grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% between now and 2027.
In addition to automotive applications, PCB boards are crucial in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and medical devices. The consumer electronics sector, driven by innovations in smartphones and wearable technology, accounts for a significant portion of PCB usage, with an estimated 40% of the market share. Moreover, in medical devices, PCBs facilitate functionalities such as monitoring and diagnostics, reflecting a growing demand for sophisticated healthcare solutions. According to industry analyses, the medical PCB market is expected to see a CAGR of over 6.5%, highlighting the critical role these boards play in the development of advanced medical technologies. These compelling statistics illustrate the versatility and essential nature of PCBs across various industries, underlining their importance in modern electronics and technology development.
Future Trends and Innovations in PCB Board Technology
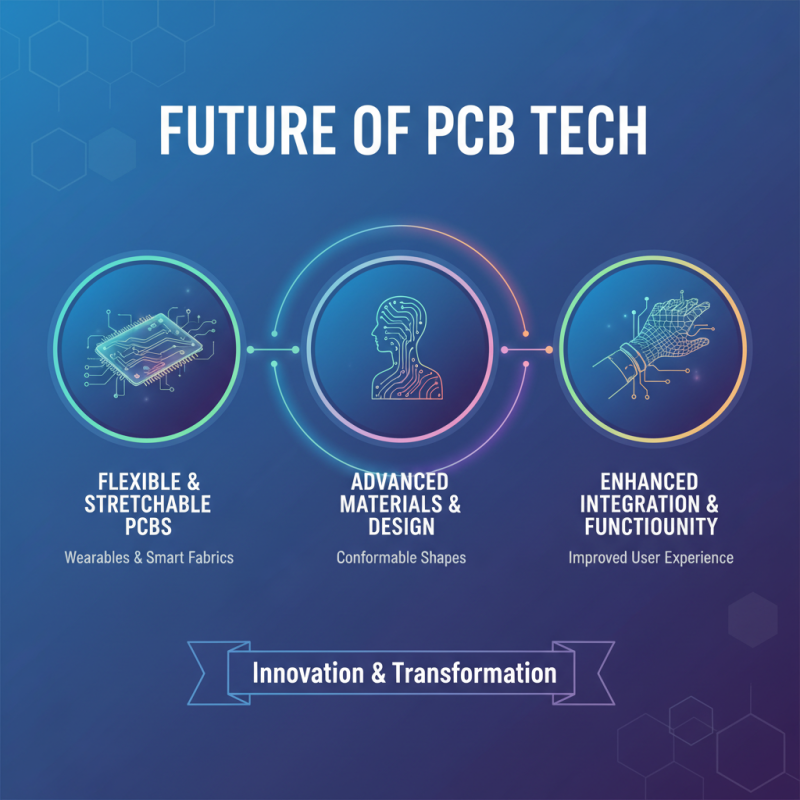
The future of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) technology promises to be both innovative and transformative, driven by advancements in materials science and design techniques. One of the most exciting trends is the development of flexible and stretchable PCBs, which cater to the growing demand for wearable electronics and smart devices. These new designs not only improve the integration of electronics into fabrics and surfaces but also enable the development of devices that can conform to various shapes, enhancing user experience and functionality.
Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning into PCB design processes is set to revolutionize the industry. By utilizing automated design tools, engineers can optimize layouts more efficiently, reducing production times and costs. Furthermore, predictive analytics will enable better decision-making by forecasting potential issues in the production and operation phases, leading to improved reliability of electronic products. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, innovations in eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes are also gaining traction, paving the way for greener and more responsible electronics production.
Related Posts
-
10 Smart Tips for Mastering PCB Circuit Design in the Digital Era
-
Addressing Common Challenges in Sourcing the Best PCB Circuits for Global Buyers
-
Exploring the Future of Printed Circuit Boards: Trends and Innovations in PCB Technology
-
Solutions for Streamlined Best Circuit Board Assembly: Achieving Excellence in Production
-
Exploring Unique Features and Applications of the Best Electronic Board Alternatives for Global Buyers
-

Benefits of Enhanced Durability in Circuit Board Manufacturing for Electronics





